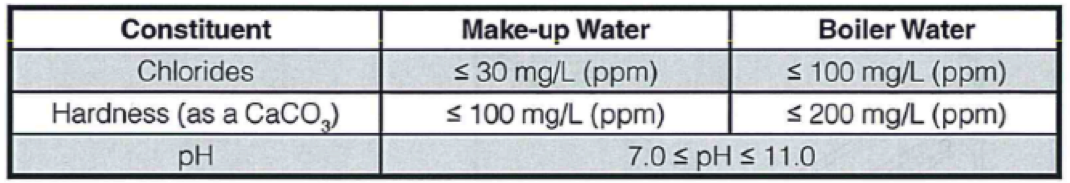
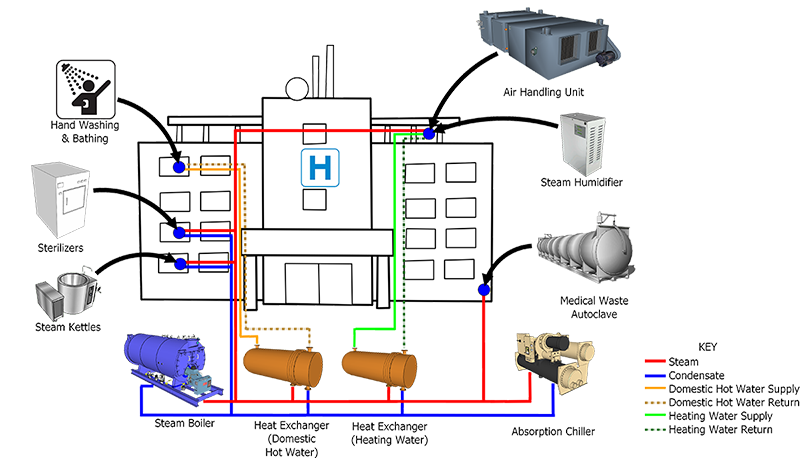
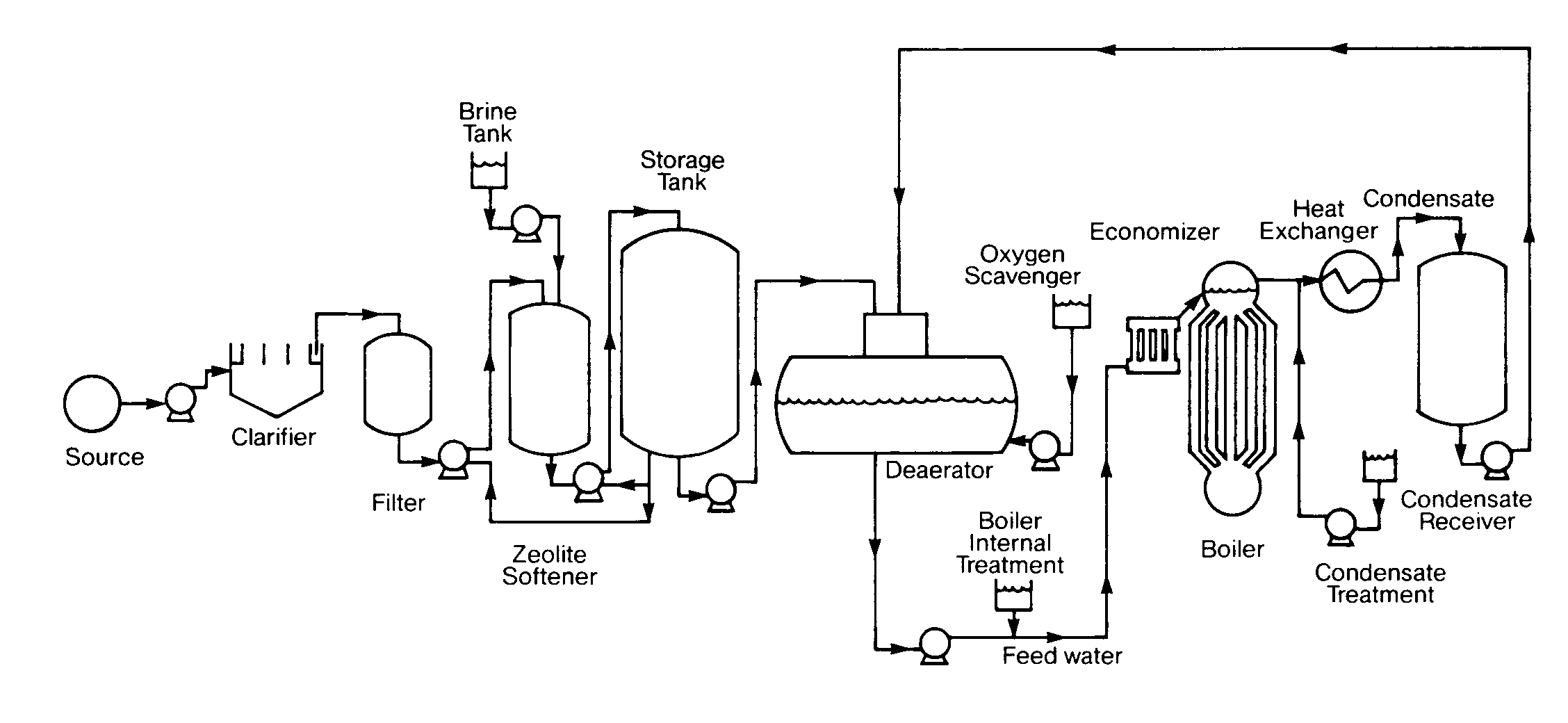
A low pressure fire tube boiler can usually tolerate high feed water hardness with proper treatment while virtually all impurities must be removed from water used in some modern high pressure boilers.
Steam boiler water hardness.
Broken down by feed water and boiler water and then by firetube.
However boiler water is deliberately softened to prevent scale formation and this gives it a propensity to foam.
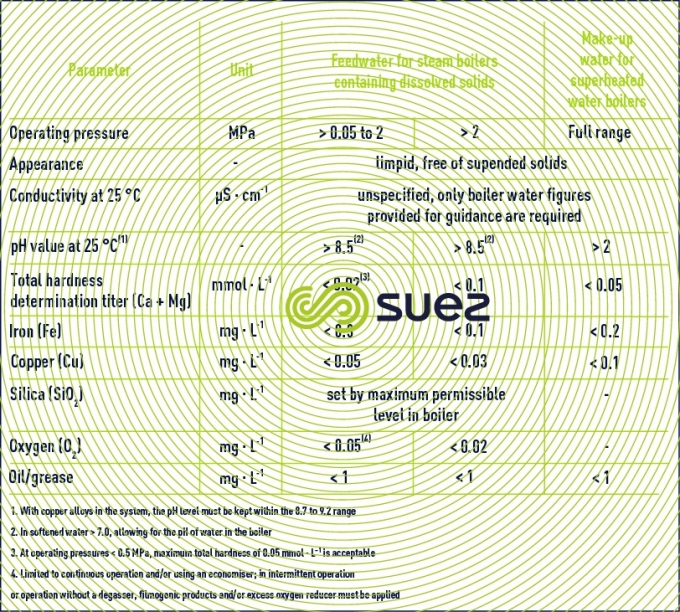
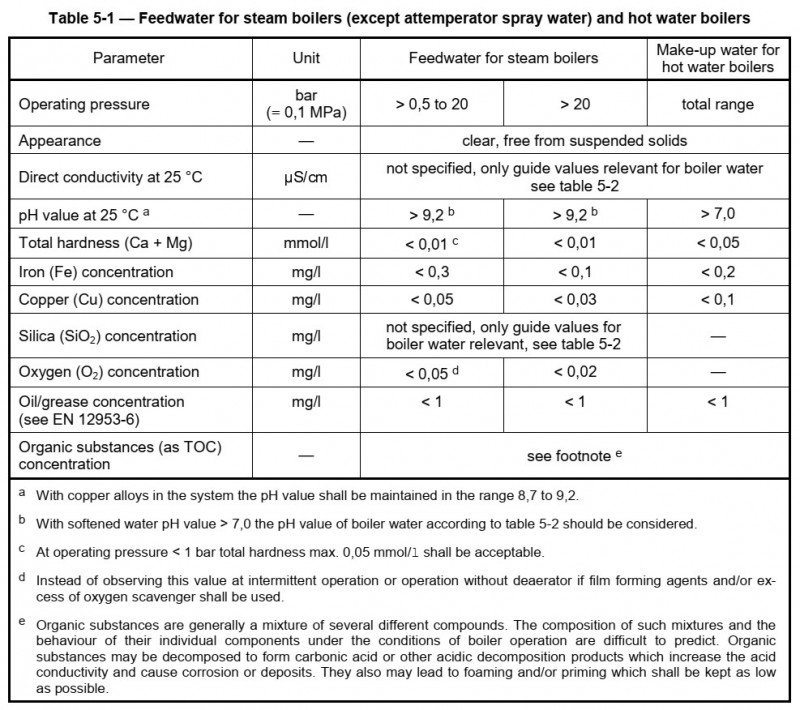
Total hardness 1 ppm maximum.
Feedwater hardness usually ranges from 0 01 to 2 0 ppm but even water of this purity does not provide deposit free operation.
Hardness hard water does not foam.
Colormetry hardness detector prevent water hardness damage to your boiler with miura s colormetry hardness detection system.
General guidelines to prevent corrosion and scaling in low pressure boilers are as follows.
Total silica 150 ppm maximum.
Phosphates are used to react with calcium hardness in the boiler water.
Milk causes violent foaming.
Colloidal particles are less than 0 000 1 mm in diameter and.
In order for this reaction to take place it is important to maintain a ph at a minimum value of 9 50.
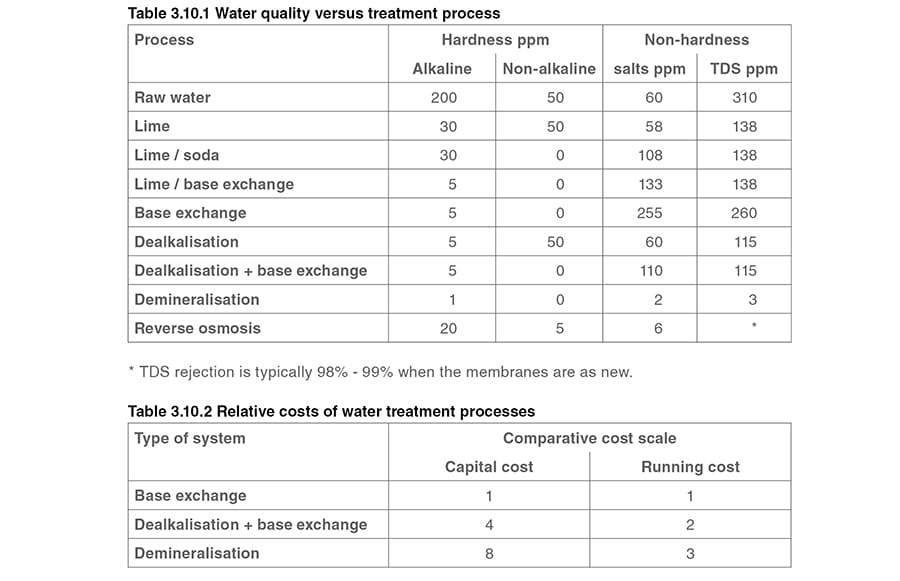
Water treatment recommendations vary depending on the operating pressure of the boiler the application steam or hot water and other parameters.
Feed water boiler water characteristics as per is 10392 1982 1 feed water parameters upto 20 kg cm2 21 kg cm2 to 39 kg cm2 40 kg cm2 to 59 kg cm2 unit total hardness 10 1 0 0 5 ppm as caco 3 ph value 8 5 9 5 8 5 9 5 8 5 9 5 dissolved oxygen.
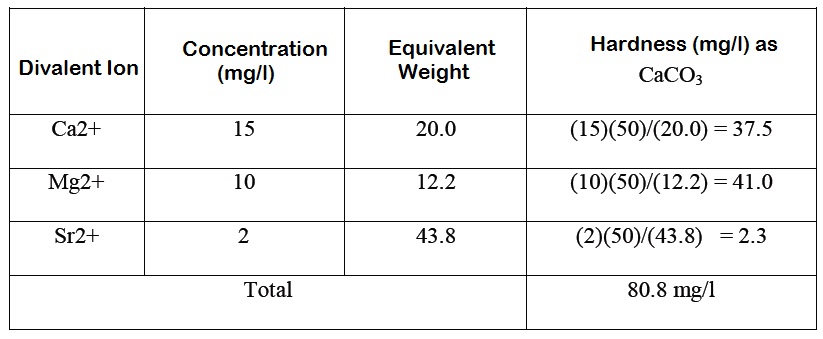
The concentration of minerals in the water is referred to as the water hardness.
Most boiler systems have sodium zeolite softened or demineralized makeup water.
Total alkalinity 600 ppm maximum.
Feed water purity requirements therefore can vary widely.
Another reason that the loss of hot boiler water is serious is because it increases the humidity in the boiler room and will contribute to the malfunction and failure of electrical controls safety devices and other electrical equipment.
Non volatile toc total organic carbon oily matter.
Colloidal substances contamination of boiler water with a colloid in suspension for example.
For boiler water the conductivity increases at the rate of approximately 2 of the value at 25 c for every 1 c increase in temperature.
Water hardness levels are typically checked manually through the use of chemical reagents but such measurements are time consuming and can result in incorrect readings.
It is desirable to keep the concentration of phosphates in the water to 30 50 ppm in order for complete reaction of the phosphates with the calcium hardness entering the.
An increase in temperature results in an increase in electrical conductivity.
This value will limit the silica content of the steam to 0 25 ppm as a function of selective.